Tunnel Boring Machines: How They Work and How They are Installed
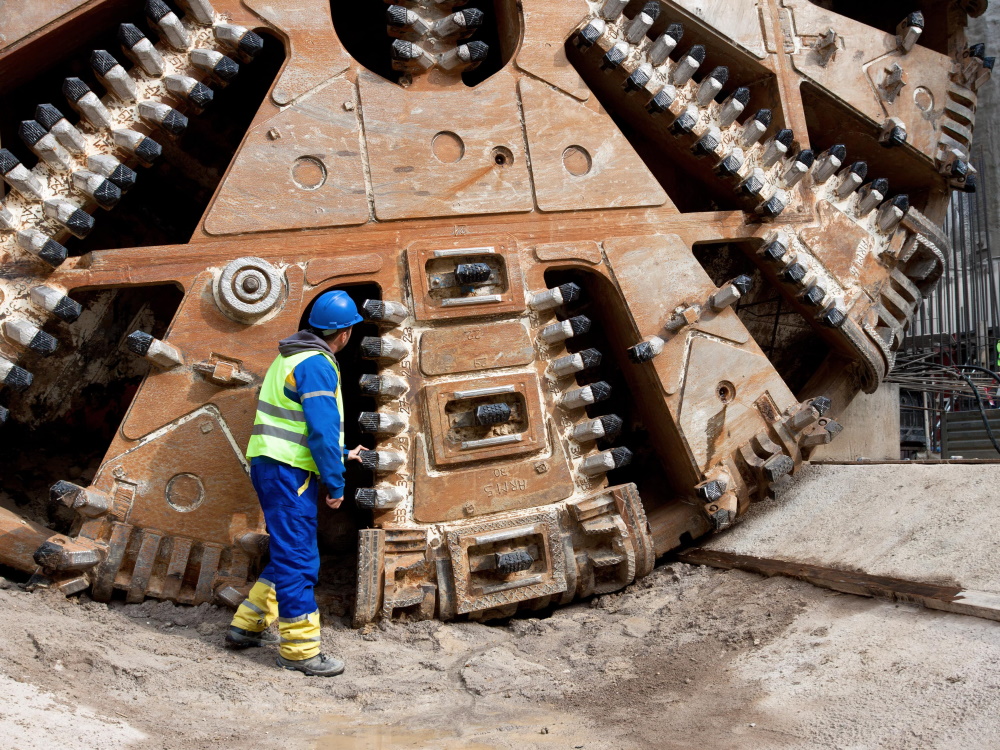

February 3, 2025
0
Introduction to Tunnel Boring Machines
Tunnel Boring Machines (TBMs) have revolutionized underground construction since they were first developed in the 19th century. These massive mechanical marvels have transformed the way we create tunnels, making previously impossible projects a reality.
From the Channel Tunnel connecting England and France to the extensive subway systems of major cities worldwide, TBMs have played a crucial role in shaping modern infrastructure.
How Tunnel Boring Machines Work

At the heart of every Tunnel Boring Machine is the cutterhead, a rotating disc equipped with cutting tools designed to excavate through various types of rock and soil. Behind the cutter head is the shield, which supports the tunnel walls as the machine advances. As the diagram below shows, the excavated material is then transported away via a conveyor system.
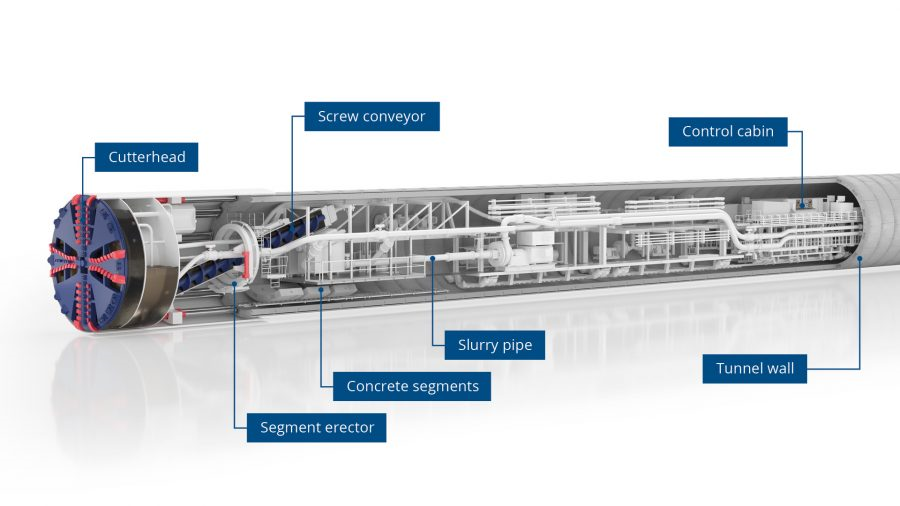
TBMs operate in a cyclical process:
- The cutter head rotates and excavates the tunnel face
- Hydraulic jacks push the machine forward
- Precast concrete segments are installed to form the tunnel lining
- The process repeats, with the TBM advancing steadily through the earth
Different types of Tunnel Boring Machines are used depending on the ground conditions.
Earth Pressure Balance Machines – Ideal for soft ground.
Hard Rock TBMs – Designed for solid rock formations.
Mixed Shield TBMs – For ground conditions that transition between hard rock and soft ground.
From Factory to Tunnel: Tunnel Boring Machine Transportation and Installation
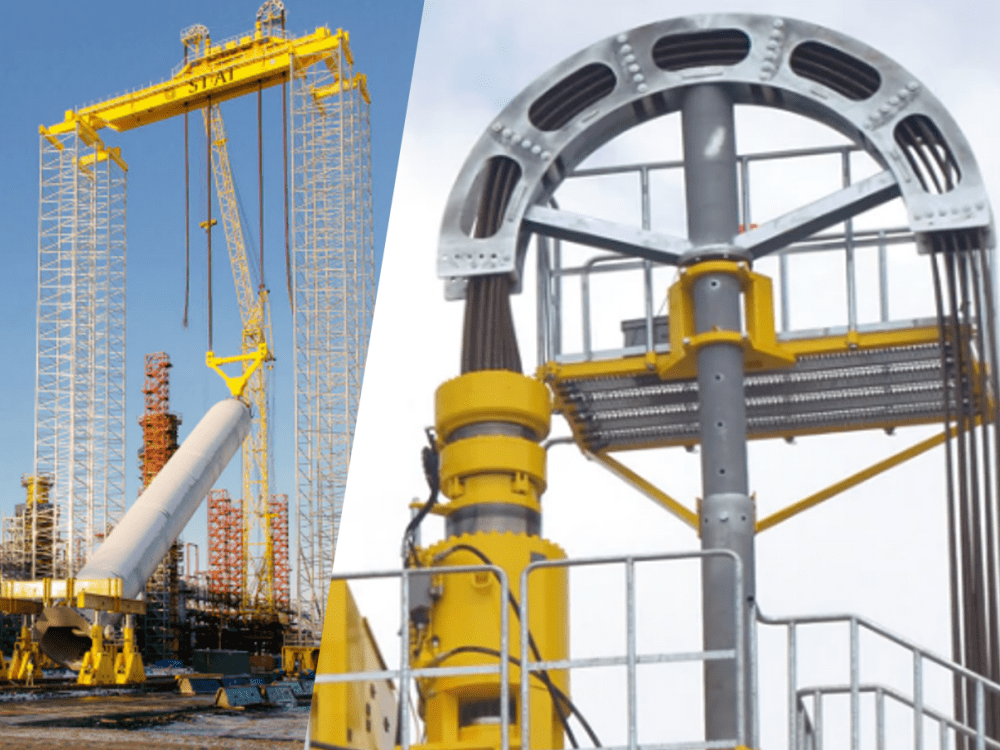
Moving a Tunnel Boring Machine from the factory to the tunnel site is an impressive logistical challenge that highlights modern-day engineering expertise.
Transportation and Assembly
TBMs are transported to project sites in modular components due to their massive size. These modules are lifted using hydraulic equipment and shipped via heavy-duty trucks, rail, or sea transport for international projects.
The installation of a Tunnel Boring Machine is a critical phase that sets the stage for the entire tunneling project. Proper planning, specialized equipment, and expert execution are essential to ensure the TBM is safely and accurately positioned to begin its underground journey.
Once on-site, the TBM typically undergoes partial assembly, including:
- Connecting major components like the cutter head and shield
- Installing electrical and hydraulic systems
- Conducting initial tests and calibrations
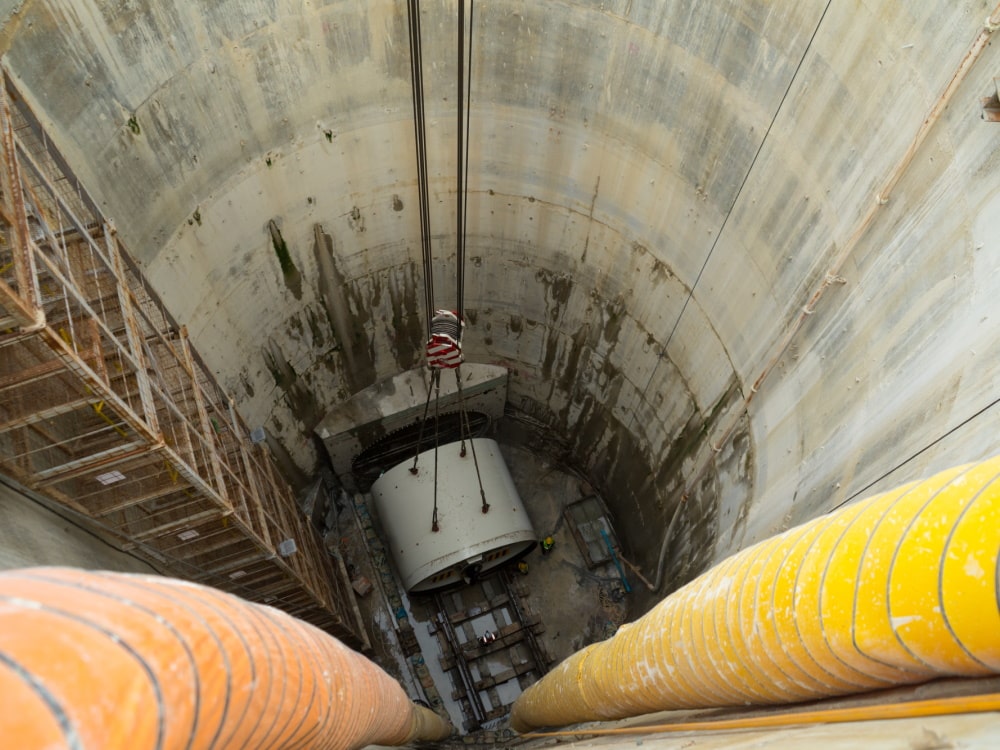
The Lowering Process
Installing a Tunnel Boring Machine involves several critical steps:
- In many cases, a launch shaft is prepared at the tunnel’s starting point.
- Heavy-lifting equipment is selected based on the TBM’s weight and site conditions and is positioned using cranes or jack-up systems
- A custom lifting frame is often fixed to the TBM’s shield for stability.
- The TBM is lowered in stages, with careful load management. Precise positioning aligns the TBM with the planned tunnel trajectory.
Case Study Links

Tunnel Boring Machine Challenges and Considerations
Several factors can complicate TBM installation:
- The center of gravity of TBM components can shift if equipment is left installed inside the shields, making lifts more challenging and potentially dangerous
- Space constraints in urban environments can affect crane operations
- Weather conditions impacting lifting safety
- The need for highly skilled personnel to ensure safe placement
- Site Preparation: Adequate preparation of the launch shaft and surrounding area
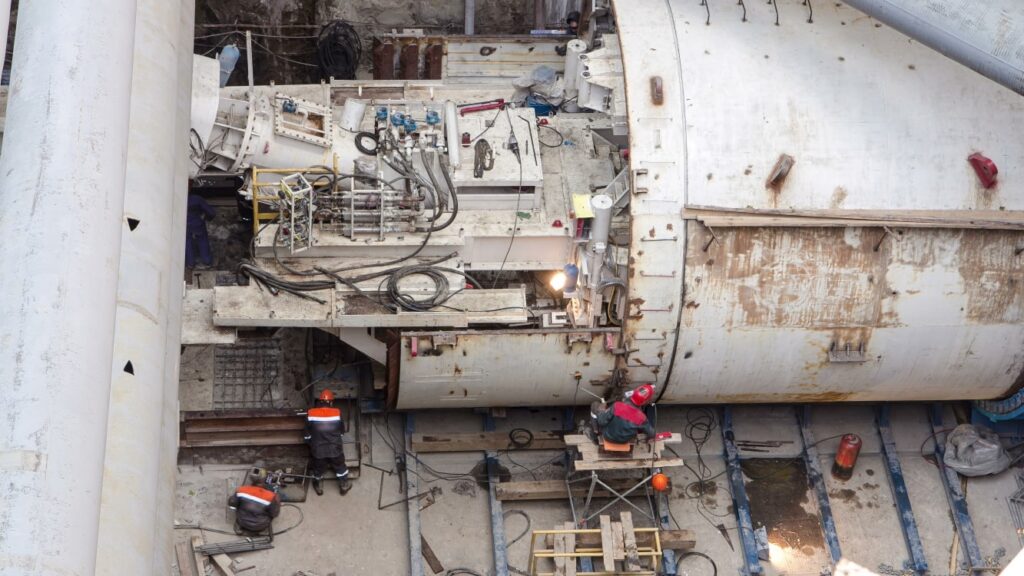

Final assembly often occurs within the tunnel itself, including installing the cutter head, drive systems, and other internal components. This entire process can span weeks to months, depending on the TBM’s size and complexity.
TBM Technology and Innovations
Recent advancements in TBM technology have focused on improving efficiency and adaptability. Modern TBMs now incorporate sophisticated sensors and control systems, allowing for real-time monitoring and adjustment of excavation parameters. Some cutting-edge features include:
- Artificial Intelligence-driven navigation systems
- Automated segment installation robots
- Hybrid TBMs capable of switching between different excavation modes
One notable innovation is the development of Multi-mode TBMs, which can adapt to changing ground conditions without the need for major modifications.
Tunnel Boring Machines and Urban Development
TBMs have become indispensable for urban development, allowing for the expansion of underground transportation networks and utilities with minimal impact on surface activities.
In densely populated cities, TBMs can create tunnels for subways, water supply, and sewage systems without the need for extensive open-cut excavations that would disrupt city life.
For instance, the Madrid Metro expansion used TBMs to add over 200 km of new lines in just a decade, significantly improving the city’s public transportation while keeping surface disruption to a minimum.
Environmental and Safety Considerations
TBMs offer significant environmental advantages over conventional tunneling methods. They produce less noise and vibration, reduce dust emissions, and minimize the amount of excavated material that needs to be transported to the surface. This results in a smaller carbon footprint for tunneling projects.
In terms of safety, Tunnel Boring Machines provide a more controlled environment for workers than alternative methods. The machine’s shield protects against cave-ins, and the automated nature of many operations reduces the need for personnel to work in potentially hazardous areas at the tunnel face.
The Future of Tunneling
The future of tunneling with TBMs looks promising and exciting. Some emerging trends could include:
- Development of autonomous TBMs that can operate with minimal human intervention
- Integration of Virtual Reality for remote operation and training
- Exploration of new applications, such as underground urban farming or data center construction
Perhaps most intriguingly, concepts could be developed for adapting TBM technology for extra-terrestrial applications. As we look towards establishing bases on the Moon or Mars, TBMs could play a crucial role in creating underground habitats protected from harsh surface conditions.

As urban populations continue to grow and infrastructure needs evolve, TBMs will undoubtedly play an increasingly important role in shaping the cities and transportation networks of the future.
Sources and Further Reading
- https://www.encardio.com/blog/TBM-method-of-tunneling
- https://www.sika.com/en/solutions-for-projects/tunnel-boring-machines.html
- https://technicore.ca/comprehensive-guide-to-efficient-tunnelling-techniques-and-technologies/
- https://crossriverrail.qld.gov.au/construction/guide-to-tunnelling/
- https://www.txintlfreight.com/digging-deep-what-are-tunnel-boring-machines/