7 On-Site Applications for an Orbital Milling Machine
November 15, 2017
0
Orbital milling machines, (sometimes referred to as circular mills), are portable machines used for large in-situ machining tasks in various industrial sectors. Their configuration is not unlike the larger flange facers in the Enerpac product line-up, with some using heavy duty and high precision bearings, mounting legs, and a radial arm with integral leadscrew for mounting the cutting tool. The key differences to a flange facer are that they use a milling head instead of a single point cutting tool, and operate with much slower rotation speed (up to 3.5ft per minute).
Below we describe 7 applications for where Mirage orbital milling machines were used successfully to solve some very challenging on-site machining problems.
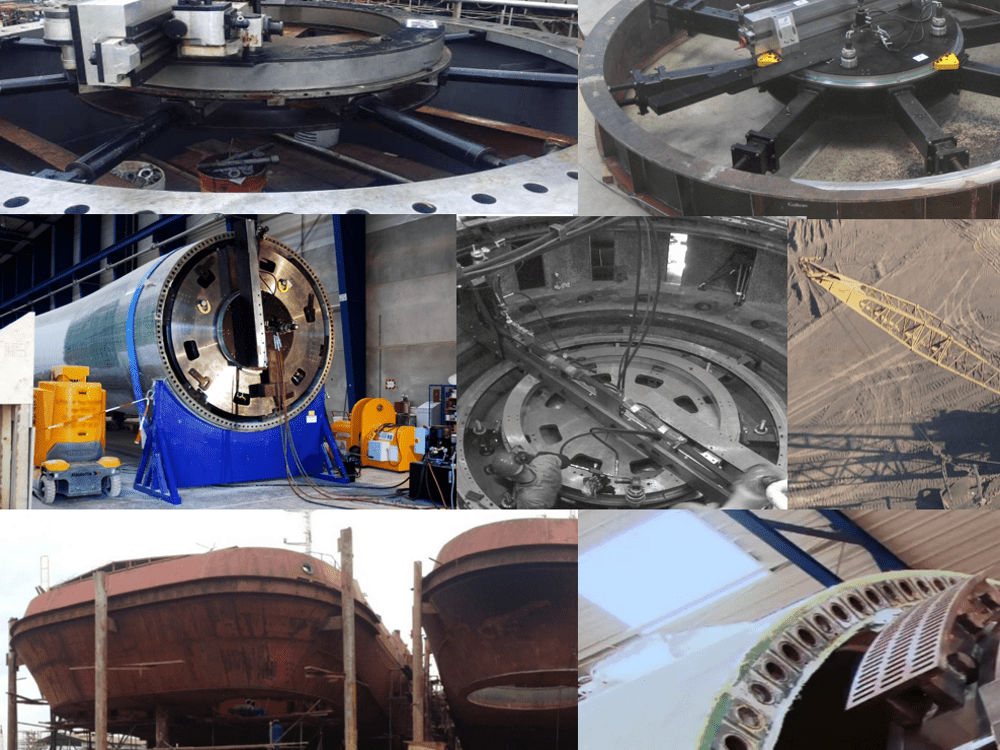
1. SHIPBUILDING INDUSTRY: THRUSTER FLANGES

Thrusters are used for either propulsion or for manoeuvring large boats and ships into position.The thruster unit is fixed to a flange built into the ship’s hull, which needs to be machined flat and smooth, to help ensure trouble free operation and maximum efficiency.
Machining of these flanges are carried out in the shipyard, requiring a robust, stable and portable machine that can produce very accurate results across a large diameter. You can find out more about this case study on our previous blog here.
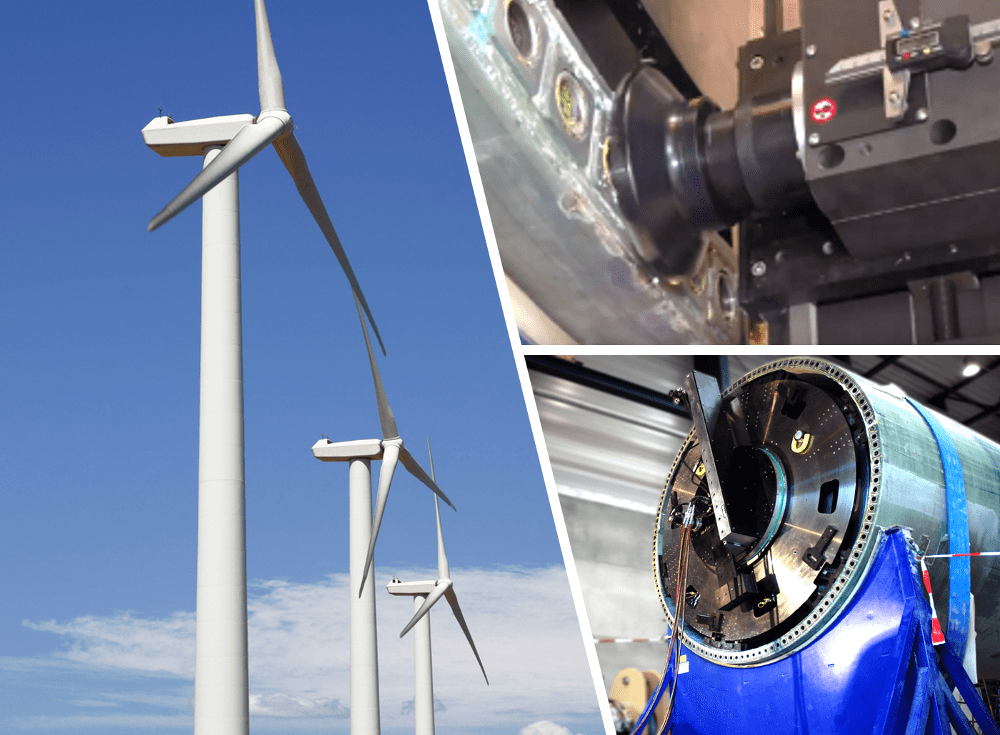
2. WIND POWER SECTOR: TURBINE BLADE MANUFACTURE

Although our orbital milling machines are classed as ‘portable’ and designed with in-situ projects in mind, Mirage has developed a range of machines designed for the manufacture of wind turbine blades. The machines are designed for a manufacturing environment where results need to be consistently accurate over a long production run.
Each blade is made from composite of glass fibre and incorporates metal inserts which need to be machined flat at the ‘root end’, where it connects to rotating hub at the top of the tower.
These specialist ‘WP’ orbital milling machines differ from the other ‘OM’ type by incorporating a hydraulically operated clamping base instead of the traditional 8 leg arrangement.
3. WIND POWER SECTOR: TOWER MANUFACTURE
.jpg?width=640&name=WP4500%20tower%20machining%20NEW%20(2).jpg)
Another application for orbital milling machines within the wind power sector is for the machining of wind towers. One example is when a leading wind tower manufacturer required the end flange of the tower to be machined within a flatness tolerance of 0.15mm at 2.7m diameter.
This project required the WP4300 orbital milling machine to clamp into the tower and machine the connecting flange. For this application, initially, a machine base using an eight jaw system was used, but later replaced with the quick set clamping type mentioned in example 2.
4. CRANE PEDESTALS
.jpg?width=640&name=CRANE%20PEDESTAL%20ORBITAL%20MILLING%20(2).jpg)
Crane pedestals are subject to incredible amounts of load, so therefore need to be perfectly flat to help ensure trouble free operation. The sheer scale of the job makes the orbital milling machine the ideal tool for machining crane pedestals in-situ at both offshore and onshore locations.
5. HYDRO POWER TURBINES

Above left: Turbine unit with stay ring shown at the top. Above right: Downhole repair inside a turbine at the Benmore Dam in New Zealand.
Hydroelectric systems produce a large amount of the world’s electricity, making them an important part of the energy-producing industries. As both the age and reliance on these systems continues to increase, the need for refurbishment of hydropower facilities increases. Mirage products have been used for such projects, with examples being turbine components, such stay rings and runner plates.
6. OFFLOADING BUOY USED WITH FPSO UNIT

Decommissioning Case Study Pack
Learn how portable machine tools solved four tough decommissioning challenges

Image by courtesy of Gunnernett via Wikimedia
Orbital milling machines have also been used to machine flanges on a Tanker Offloading Buoy. These units connect to the Floating Production and Storage and Offloading (FPSO) vessels and include large rotating sections with integral flanges.
7. DRAGLINE REPAIR
.jpg?width=640&name=dragline-in-quarry%20(2).jpg)
As with the oil rig crane pedestal faces mentioned previously, the same operation can be carried out on dragline plant equipment using a large orbital milling machine such as the OM6000.
ORBITAL MILLING ESSENTIALS
- Orbital milling machines are available in 2 types: OM and WP (wind power).
- They are typically used for diameters up to 8m (315”).
- They can be mounted in the horizontal or vertical orientation including upside down.
- Some ID mount flange facers can be converted to an orbital milling machine using an optional conversion kit.
- They are usually hydraulically powered, so need to be used with a hydraulic power pack.
- Special bases can be designed for applications requiring a repeatable quick set up.
- Flatness tolerance example: (wind tower machining) of 0.15mm at 2.7m diameter.
- Surface cutting speed up to 3.5ft per minute.
Do you need equipment for an on-site machining project? Contact Enerpac here